Description
World's first molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) grown MoS2 monolayers. MBE is an epitaxial method for single-crystal quality film deposition which offers high crystallinity and reduced defect density compared to chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) techniques (see HRTEM images below). MBE growth of MoS2 monolayers take place in a MBE chamber at a base pressure of 8E-9 Torr and deposition rate is extremely slow (5-100 atoms per second) to reach structural perfection. Typical MBE growth produces monolayer thick MoS2 isolated triangles on double-side polished c-cut sapphire. Currently, MBE MoS2 is only offered on sapphire substrates but in the near future our MBE substrates will also include mica, graphite, and gold.
Comparison between MBE, CVD, and MOCVD

TEM comparison between MBE, CVD, and MOCVD

Optical images collected from MBE MoS2

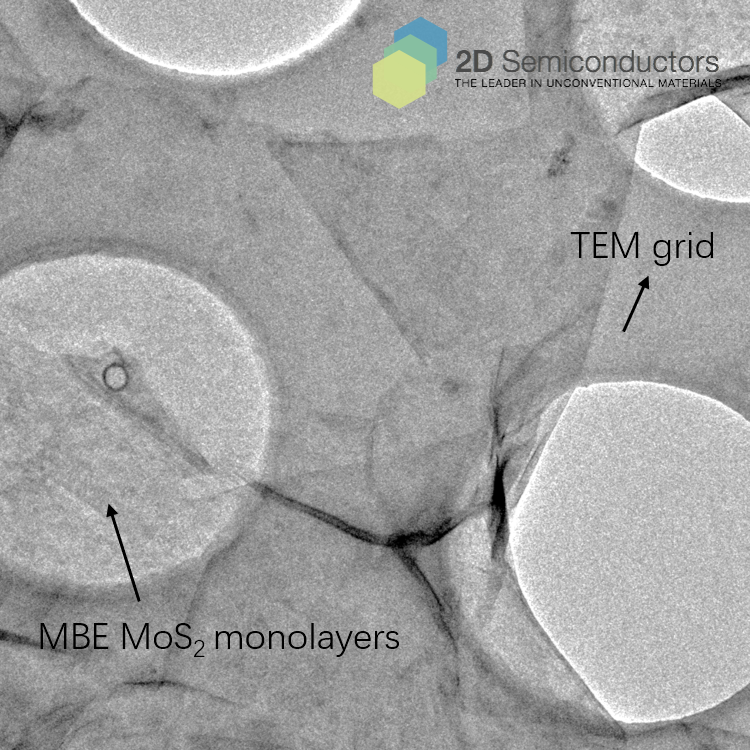
MBE MoS2 suspended on TEM grid
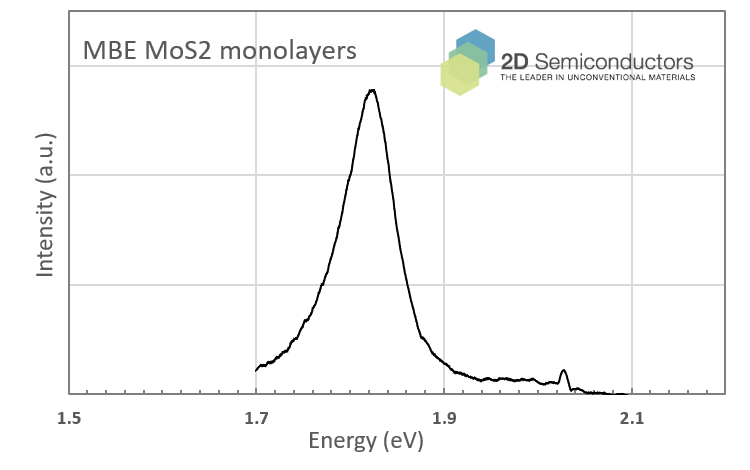
PL spectrum collected from MBE MoS2
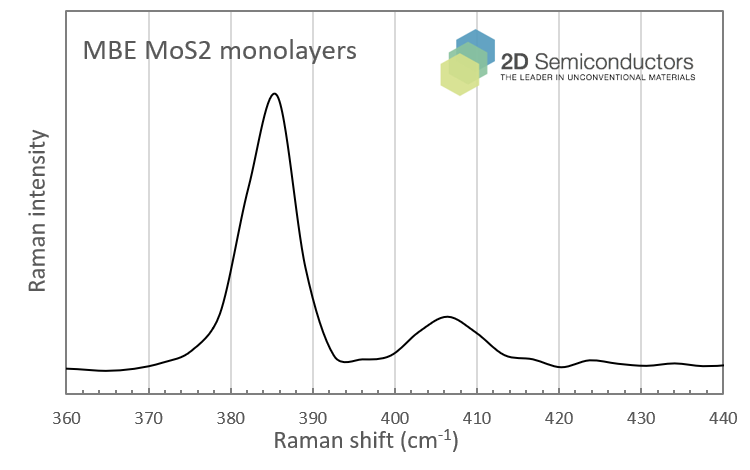
Raman spectrum collected from MBE MoS2
Sample Properties
| Sample size | 1cm x 1cm square shaped |
| Substrate type | Double side polished c-cut sapphire |
| Coverage | Isolated triangles but may reach some continuity |
| Electrical properties | Direct gap excitonic semiconductor |
| Crystal structure | Hexagonal Phase |
| Unit cell parameters | a = b = 0.33 nm, c = 1.292 nm, α = β = 90°, γ = 120° |
| Production method | Molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) |
| Characterization methods | Raman, photoluminescence, TEM, XRD, and others |
Additional Information
Elements: |
Mo,S |
Element: |
Molybdenum |
Element: |
Sulfur |
Formula: |
MoS2 |
Material class: |
MX2 |
Material class: |
Dichalcogen |
Properties: |
Semiconductor |
Properties: |
Excitonic |
Band gap range: |
VIS |
Growth method: |
MBE |
Doping: |
Undoped |
Thin-film type: |
Monolayer |
Thin-film type: |
Triangles |
Substrate: |
Sapphire |





















