Description
Single crystal ReS₂ (Rhenium disulfide) crystals are developed at our facilities using chemical vapor transport or flux zone technique methods after 9 years of growth optimization to ensure anisotropic properties. Our ReS2 crystals display impressive structural anisotropy from bulk down to monolayers as evidenced by TEM and angle resolved Raman spectroscopy measurements (see XRD, TEM, Raman, PL, and other figures below). Crystals are rather large in size, perfectly layered, and ready for exfoliation. Our R&D team also provides you with transfer technique to boost your monolayer yield rate up to 95%. If your research needs doped ReS2 crystals, we can introduce Mo, Au, Nb, and other dopants.
Typical characteristics of ReS2 crystals from 2Dsemiconductors
| Crystal size | 5-7 mm in size |
| Dopants | intrinsic semiconductor (for doping, please contact us) |
| Material properties | ~1.4 eV emission (300K), direct/indirect gap semiconductor |
| Crystal structure | 1T' phase (anisotropic semiconductor) |
| Unit cell parameters | a=0.633 nm, b=0.638 nm, c=0.665 nm; α=106.7°, β=119°, γ=89.98° |
| Growth method | [Default] Flux zone (no halide contamination) defect free [Optional CVT]: Contains Br2, Cl2, TeCl4, and other halides |
| Purity |
99.9999% confirmed
|
Growth method matters> Flux zone or CVT growth method? Contamination of halides and point defects in layered crystals are well known cause for their reduced electronic mobility, reduced anisotropic response, poor e-h recombination, low-PL emission, and lower optical absorption. Flux zone technique is a halide free technique used for synthesizing truly semiconductor grade vdW crystals. This method distinguishes itself from chemical vapor transport (CVT) technique in the following regard: CVT is a quick (~2 weeks) growth method but exhibits poor crystalline quality and the defect concentration reaches to 1E11 to 1E12 cm-2 range. In contrast, flux method takes long (~3 months) growth time, but ensures slow crystallization for perfect atomic structuring, and impurity free crystal growth with defect concentration as low as 1E9 - 1E10 cm-2. During check out just state which type of growth process is preferred. Unless otherwise stated, 2Dsemiconductors ships Flux zone crystals as a default choice.
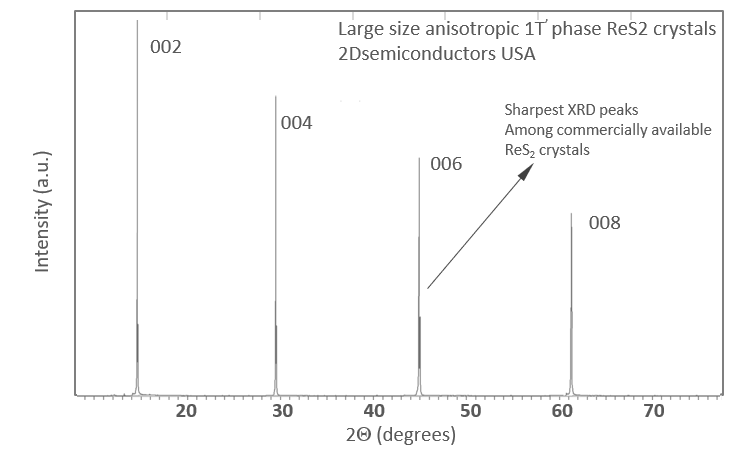
XRD data collected from ReS2 crystals
Raman spectrum collected from ReS2 monolayers

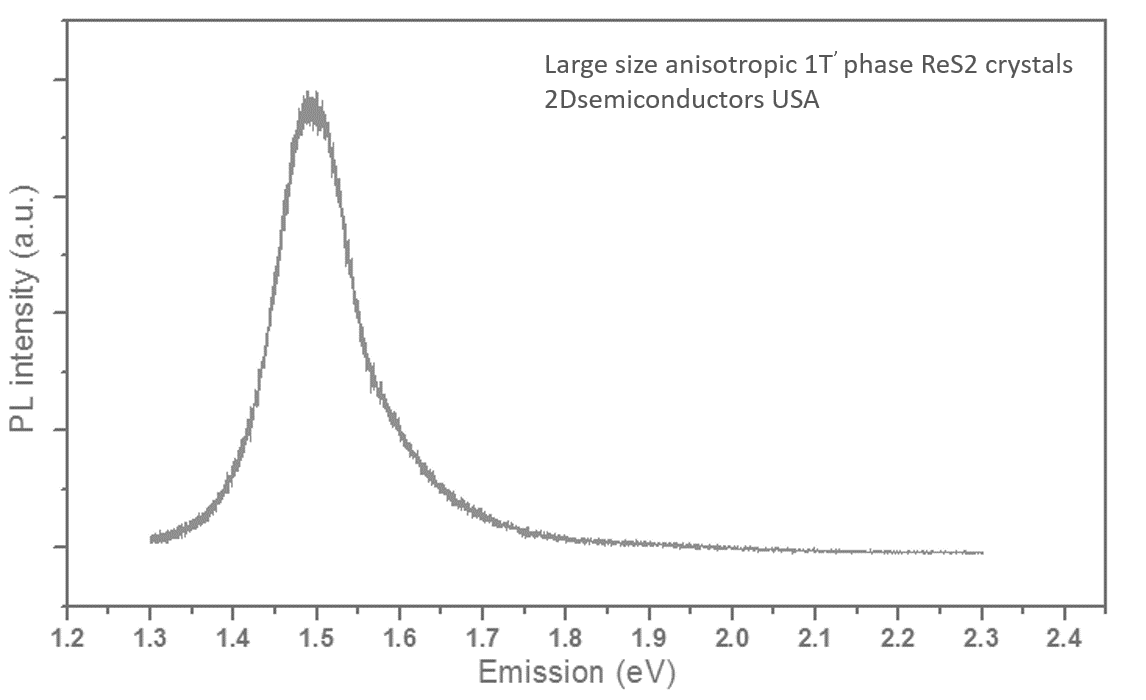
PL spectrum collected from ReS2 on SiO2/Si substrates
SIMS purity datasets collected from ReS2 crystals

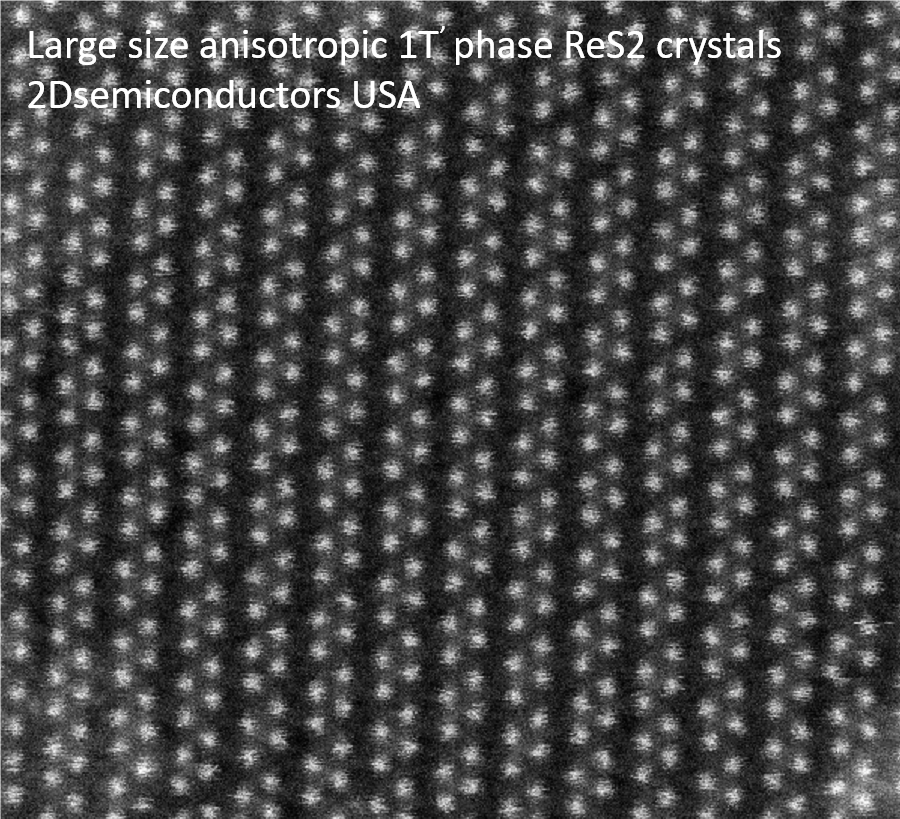
HRTEM images collected from ReS2 crystals
"High Responsivity Phototransistors Based on Few-Layer ReS2 for Weak Signal Detection"
Advanced Functional Materials https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201504408
D. Wolverson et,al. "Rhenium Dichalcogenides: Layered Semiconductors with Two Vertical Orientations," Nano Letters 2016, 16, 1381−1386
Ignacio Gutiérrez-Lezama et. al. "Electroluminescence from indirect band gap semiconductor ReS2" 2D Materials, Volume 3, Number 4
Manish Chhowalla, "Two-dimensional semiconductors for transistors" Nature Reviews Materials 1, Article number: 16052 (2016) doi:10.1038/natrevmats.2016.52
Q. Cui et. al. "Coherent Control of Nanoscale Ballistic Currents in Transition Metal Dichalcogenide ReS2" ACS Nano 10.1021/acsnano.5b01111 (2015)
X-F. Qiao et.al. "Polytypism and unexpected strong interlayer coupling in two-dimensional layered ReS2" Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 8324 (2016)
D. Wolverson et.al. "Raman Spectra of Monolayer, Few-Layer, and Bulk ReSe2: An Anisotropic Layered Semiconductor" ACS Nano, 2014, 8 (11), pp 11154–11164
E. Lorchat et.al. "Splitting of Interlayer Shear Modes and Photon Energy Dependent Anisotropic Raman Response in N-Layer ReSe2 and ReS2" ACS Nano, 2016, 10 (2), pp 2752–2760
Additional Information
Elements: |
Re,S |
Element: |
Rhenium |
Element: |
Sulfur |
Formula: |
ReS2 |
Material class: |
MX2 |
Material class: |
Dichalcogen |
Material class: |
Quasi-1D |
Properties: |
Semiconductor |
Properties: |
Excitonic |
Band gap range: |
VIS |
Growth method: |
Flux |
Growth method: |
CVT |
Doping: |
Undoped |
Doping: |
p-Type |
Doping: |
n-Type |























